内容规划总共分为三个章节来写,分别运行环境构建、利用Web应用管理索引以及Web应用管理数据三大块来说明。
具体有:
[这些操作都是在CentOS下操作的,主要带大家熟悉下Elasticsearch环境]
- 1.1.下载& Linux下ElasticSearch安装
- 1.2.中文分词插件IK
- 1.3.索引
- 1.4.如何数据管理
[在Springboot环境下,利用JAVA环境操作索引]
- 2.1.新增索引
- 2.2.查询索引
- 2.3.删除索引
[在Springboot环境下,管理数据]
- 3.1.WEB HTTP提交数据<单条提交、批量提交>
- 3.2.WEB HTTP方式条件查询
- 3.3.WEB HTTP删除数据


2. SpringBoot集成
开发工具,这里选择的是IDEA 2019.2,构建Maven工程等一堆通用操作,不清楚的自行百度。
2.1. POM配置
我这边选择 elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client 方式来集成,发现这有个坑,开始没注意,踩了好久,就是要排除掉 elasticsearch、elasticsearch-rest-client ,这里没有选择 spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch ,因为最新版的 starter 现在依然是6.x版本号,并没有集成 elasticsearch7.4.0,导致使用过程中有很多版本冲突,读者在选择的时候多加留意。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
|
2.2. yml配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| server:
port: 9090
spring:
datasource:
name: mysql
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
druid:
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 5
max-active: 20
max-wait: 30000
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
validation-query: select 1
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
pool-prepared-statements: false
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=6000
es:
host: 192.168.147.132
port: 9200
scheme: http
mybatis:
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/**/*.xml
|
这里定义 es 节点下即 elasticsearch 的地址端口信息,修改为自己的即可。
2.3. 核心操作类
为了规范索引管理,这里将所有的操作都封装成一个基类,实现对索引的增删改查。同时还集成了对数据的单个以及批量的插入以及删除。避免针对每个索引都自己写一套实现,杜绝代码的冗余,同时这样的集成对代码的结构本身也是低侵入性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
| package xyz.wongs.weathertop.base.dao;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.support.IndicesOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.Settings;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.index.reindex.DeleteByQueryRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import sun.rmi.runtime.Log;
import xyz.wongs.weathertop.base.entiy.ElasticEntity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class BaseElasticDao {
@Autowired
RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
public void createIndex(String idxName,String idxSQL){
try {
if (!this.indexExist(idxName)) {
log.error(" idxName={} 已经存在,idxSql={}",idxName,idxSQL);
return;
}
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest(idxName);
buildSetting(request);
request.mapping(idxSQL, XContentType.JSON);
CreateIndexResponse res = restHighLevelClient.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
if (!res.isAcknowledged()) {
throw new RuntimeException("初始化失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(0);
}
}
public boolean indexExist(String idxName) throws Exception {
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest(idxName);
request.local(false);
request.humanReadable(true);
request.includeDefaults(false);
request.indicesOptions(IndicesOptions.lenientExpandOpen());
return restHighLevelClient.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
public void buildSetting(CreateIndexRequest request){
request.settings(Settings.builder().put("index.number_of_shards",3)
.put("index.number_of_replicas",2));
}
public void insertOrUpdateOne(String idxName, ElasticEntity entity) {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest(idxName);
request.id(entity.getId());
request.source(JSON.toJSONString(entity.getData()), XContentType.JSON);
try {
restHighLevelClient.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void insertBatch(String idxName, List<ElasticEntity> list) {
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
list.forEach(item -> request.add(new IndexRequest(idxName).id(item.getId())
.source(JSON.toJSONString(item.getData()), XContentType.JSON)));
try {
restHighLevelClient.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public <T> void deleteBatch(String idxName, Collection<T> idList) {
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
idList.forEach(item -> request.add(new DeleteRequest(idxName, item.toString())));
try {
restHighLevelClient.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public <T> List<T> search(String idxName, SearchSourceBuilder builder, Class<T> c) {
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest(idxName);
request.source(builder);
try {
SearchResponse response = restHighLevelClient.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHit[] hits = response.getHits().getHits();
List<T> res = new ArrayList<>(hits.length);
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
res.add(JSON.parseObject(hit.getSourceAsString(), c));
}
return res;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteIndex(String idxName) {
try {
if (!this.indexExist(idxName)) {
log.error(" idxName={} 已经存在",idxName);
return;
}
restHighLevelClient.indices().delete(new DeleteIndexRequest(idxName), RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteByQuery(String idxName, QueryBuilder builder) {
DeleteByQueryRequest request = new DeleteByQueryRequest(idxName);
request.setQuery(builder);
request.setBatchSize(10000);
request.setConflicts("proceed");
try {
restHighLevelClient.deleteByQuery(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
3. 实战
通过以上的集成,我们看到完成在项目中对 elasticsearch 的集成,同时也用基类,将所有可能的操作都封装起来。下来我们通过对基类的讲解,来逐个说明!
3.1. 索引管理
由于在BaseElasticDao类中createIndex方法,我在Controller层将索引名称和索引SQL封装过,详细见Github演示源码 中xyz.wongs.weathertop.palant.vo.IdxVo
3.1.1. 创建索引
我们在创建索引过程中需要先判断是否有这个索引,否则不允许创建,由于我案例采用的是手动指定indexName和Settings,大家看的过程中要特别注意下,而且还有一点indexName必须是小写,如果是大写在创建过程中会有错误

。详细的代码实现见如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
@RequestMapping(value = "/createIndex",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseResult createIndex(@RequestBody IdxVo idxVo){
ResponseResult response = new ResponseResult();
try {
if(!baseElasticDao.indexExist(idxVo.getIdxName())){
String idxSql = JSONObject.toJSONString(idxVo.getIdxSql());
log.warn(" idxName={}, idxSql={}",idxVo.getIdxName(),idxSql);
baseElasticDao.createIndex(idxVo.getIdxName(),idxSql);
} else{
response.setStatus(false);
response.setCode(ResponseCode.DUPLICATEKEY_ERROR_CODE.getCode());
response.setMsg("索引已经存在,不允许创建");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
response.setStatus(false);
response.setCode(ResponseCode.ERROR.getCode());
response.setMsg(ResponseCode.ERROR.getMsg());
}
return response;
}
|
创建索引需要设置分片,这里采用Settings.Builder方式,当然也可以JSON自定义方式,本文篇幅有限,不做演示。查看xyz.wongs.weathertop.base.service.BaseElasticService.buildSetting方法,这里是默认值。
index.number_of_shards:分片数
number_of_replicas:副本数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public void buildSetting(CreateIndexRequest request){
request.settings(Settings.builder().put("index.number_of_shards",3)
.put("index.number_of_replicas",2));
|
这时候我们通过Postman工具调用Controller,发现创建索引成功。
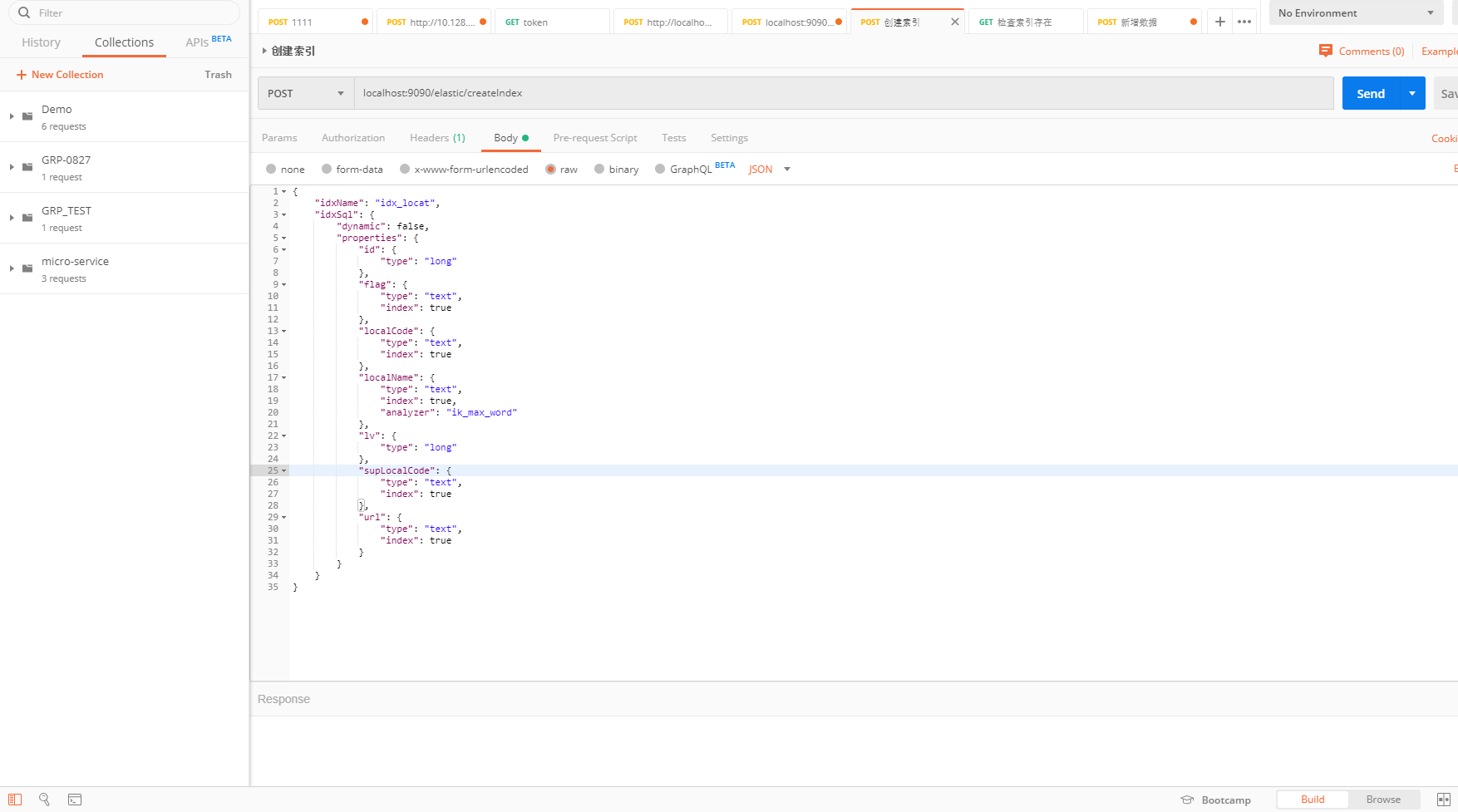
再命令行执行**curl -H “Content-Type: application/json” -X GET “http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"**,效果如图:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
[elastic@localhost elastic]$ curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
yellow open twitter scSSD1SfRCio4F77Hh8aqQ 3 2 2 0 8.3kb 8.3kb
yellow open idx_location _BJ_pOv0SkS4tv-EC3xDig 3 2 1 0 4kb 4kb
yellow open wongs uT13XiyjSW-VOS3GCqao8w 3 2 1 0 3.4kb 3.4kb
yellow open idx_locat Kr3wGU7JT_OUrRJkyFSGDw 3 2 3 0 13.2kb 13.2kb
yellow open idx_copy_to HouC9s6LSjiwrJtDicgY3Q 3 2 1 0 4kb 4kb
|
说明创建成功,这里总是通过命令行来验证,有点繁琐,既然我都有WEB服务,为什么不直接通过HTTP验证了?
3.1.2. 查看索引
我们写一个对外以HTTP+GET方式对外提供查询的服务。存在为TRUE,否则False.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
@RequestMapping(value = "/exist/{index}")
public ResponseResult indexExist(@PathVariable(value = "index") String index){
ResponseResult response = new ResponseResult();
try {
if(!baseElasticDao.isExistsIndex(index)){
log.error("index={},不存在",index);
response.setCode(ResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_EXIST.getCode());
response.setMsg(ResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_EXIST.getMsg());
} else {
response.setMsg(" 索引已经存在, " + index);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
response.setCode(ResponseCode.NETWORK_ERROR.getCode());
response.setMsg(" 调用ElasticSearch 失败!");
response.setStatus(false);
}
return response;
}
|
3.1.3. 删除索引
删除的逻辑就比较简单,这里就不多说。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public void deleteIndex(String idxName) {
try {
if (!this.indexExist(idxName)) {
log.error(" idxName={} 已经存在",idxName);
return;
}
restHighLevelClient.indices().delete(new DeleteIndexRequest(idxName), RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
|
4. 源码
Github演示源码 ,记得给Star
Gitee演示源码,记得给Star




